The magnetic field experiment IMSC
IMSC is composed of 3 orthogonal magnetic antennae
(search coil type) linked to a pre-amplifier unit with a shielded cable of
80cm. (see Figure 1). The search coil magnetometer consists of a core in permalloy (high permeability
material) on which are wound a main coil with several thousand turns (12000) of
copper wire and a secondary coil with a few turns. The core is a ![]() where µreff is the relative effective permeability, N
the number of wire turns, S the cross section of the core, B the magnetic
induction outside the core, aligned with the core. The coefficient µreff strongly depends on the ratio between the
length and the diameter of the core, and on the permeability of the core. The
secondary coil is used as a flux feedback, to create a flat frequency response
on a bandwidth centred on the resonance frequency of the main coil. An
electrostatic screen (comb shaped flexible printed circuit) connected to the
signal ground maintains a uniform potential around the windings. The rod, the
windings, the electrostatic screen, and the output cable are potted inside an
epoxy tube (
where µreff is the relative effective permeability, N
the number of wire turns, S the cross section of the core, B the magnetic
induction outside the core, aligned with the core. The coefficient µreff strongly depends on the ratio between the
length and the diameter of the core, and on the permeability of the core. The
secondary coil is used as a flux feedback, to create a flat frequency response
on a bandwidth centred on the resonance frequency of the main coil. An
electrostatic screen (comb shaped flexible printed circuit) connected to the
signal ground maintains a uniform potential around the windings. The rod, the
windings, the electrostatic screen, and the output cable are potted inside an
epoxy tube (
In the VLF range, the flat frequency response of the
frequency band is going from 100 Hz up to 17.4 kHz. These are the cut-off
frequencies at 3dB, the slopes of the filter being +6
dB/octave and -12 dB/octave, respectively.
In order to check the good operation of the antennas,
a calibration sequence can be implemented when the experiment is switched on
and then every 4, 8 or 12 minutes (fixed by telecommand).
During this sequence a sum of two sinusoids at 625 Hz and 10 kHz is sent during
one second in burst mode and four seconds in survey mode.

Figure 1: The magnetic search-coil IMSC and its
pre-amplifier.
The strategy to record the data
There are two main modes of operation: a burst mode
which is triggered when the satellite is above given seismic zones (see Figure
4), and elsewhere a survey mode. The corresponding recorded data are
•
in the
BURST MODE
–
waveforms
of the three magnetic components in the ELF range up to 1 kHz,
–
waveforms
of one magnetic component (selected among the three by telecommand)
in the VLF range up to 17 kHz,
•
in the
SURVEY MODE
–
spectra of one magnetic component (selected among the three by telecommand) up to 17 kHz. Three possible combinations of
frequency and time resolutions can be selected by telecommand
(see table 1).
|
Type |
Samples ( FFT input) |
Average spectra |
Time resolution |
Average frequencies |
Frequency resolution |
Points of spectrum |
TM flow |
|
0 |
2048 |
40 |
2.048 s |
1 |
19.53 Hz |
1024 |
4 kb/s |
|
1 |
2048 |
10 |
0.512 s |
1 |
19.53 Hz |
1024 |
16 kb/s |
|
2 |
2048 |
40 |
2.048 s |
4 |
78.125 Hz |
256 |
1 kb/s |
Table 1. VLF
spectrogram characteristics in Survey mode.
It must be noted that during the burst mode and for simplification of the
data processing, a VLF spectrum similar to the one which is calculated in
survey mode can be implemented. Before the FFT, a Blackman-Harris window is
applied on the samples.
In addition, whatever is the mode, either a magnetic or an electric component
in the VLF range is used as input for the onboard neural network
.
The ELF and VLF waveforms are sent in telemetry with 2 bytes resolution.
The averaged spectrum values Gv(k)
onboard the scientific payload computer are with four bytes and to reduce this
dynamic in the telemetry, a logarithmic compression on one byte is done in
order to have a power with 256 levels which can be directly transform in an
image with 256 colors. Then all frequency components
of the VLF spectrum (256 or 1024) GTM(k) given
by
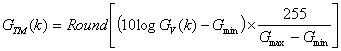
where Round(x)
gives the nearest integer to x, are sent in telemetry as bytes together with
the two gains (a minimum Gmin and a
maximum value Gmax which can be modified
by telecommand) which are used to increase the
dynamic. Then the classical transfer function is applied to obtain physical
values.
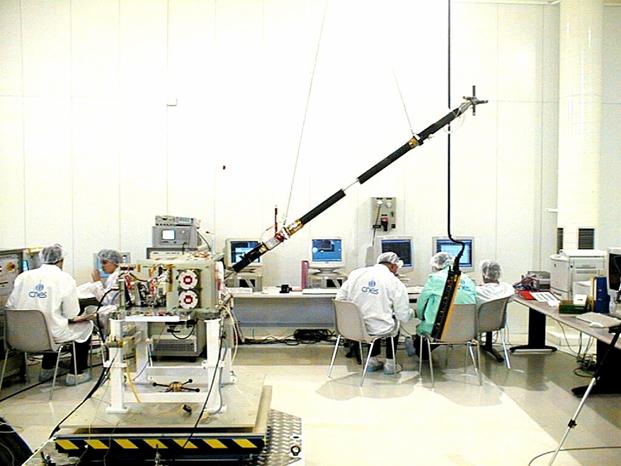

Figure 2: IMSC mounted at the end of its boom during integration tests.
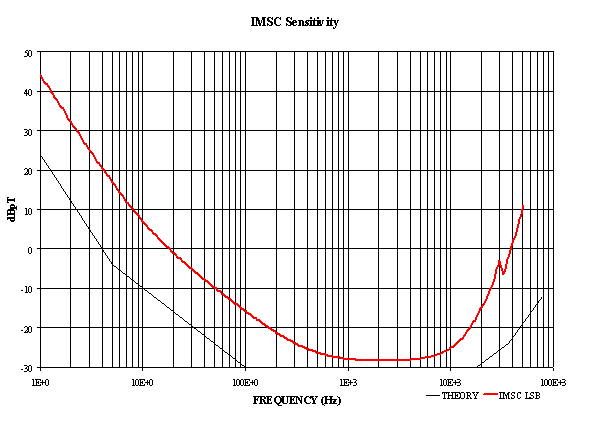
Figure 3: Sensitivity of the
search-coil antenna as function of frequency. The black curve is related to the
theory and the red curve includes the complete chain of analysis.
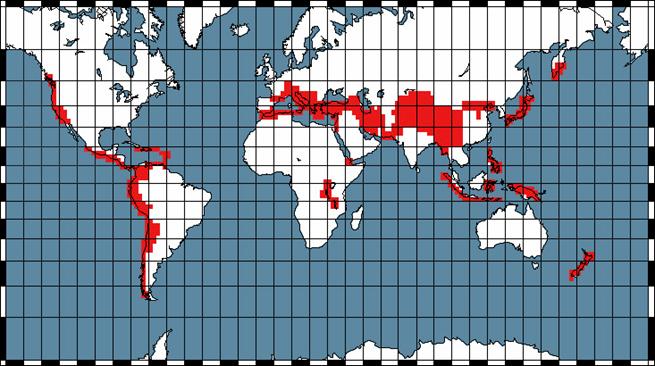
Figure 4: The zones where the experiment will be in burst are indicated
in red.